Research Progress
Spectrum sensing plays an important role in future wireless communication systems as it helps to resolve the coexistence issue and optimize spectrum efficiency. However, the ongoing 5G communication involves diversified scenarios with different characteristics and diverse requirements, which makes spectrum sensing methods difficult to serve various applications flexibly while maintaining satisfactory performance. The scarcity of spectrum resource remains a critical challenge for 5G communications.
Motivated by such a challenge, a research team led by Prof. HU Honglin and Prof. XU Tianheng at Shanghai Advanced Research Institute (SARI) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences provided a novel spectrum sensing technique, seeking a feasible way to combine the reinforcement learning concept with advanced spectrum sensing methods so as to optimize the performance of the cognitive radio network under multifarious scenarios in 5G communications. The research results were published in the latest issue of IEEE Wireless Communications entitled “Intelligent Spectrum Sensing: When Reinforcement Learning Meets Automatic Repeat Sensing in 5G Communications.”
The research team analyzes different requirements of several typical 5G scenarios, and categorizes three dedicated models with respective optimization targets for spectrum sensing techniques. In order to be adaptive for various optimization targets, scientists have designed the architecture for the intelligent spectrum sensing technique, trying to take account of both instability and adaptability issues. Numerical results manifested that the proposed sensing technique has the capability of adapting to various scenarios with different optimization targets.
The research results are promising for practical applications. They have been applied in the SEANET system developed by CAS and Alpha, a campus network constructed by CAS and ShanghaiTech University. The results also contribute to further deployment and promotion of 5G and next generation communication system in China.
This research was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Shanghai Rising-Star Program, the Shanghai Young Talent Sailing Program and the Program of Shanghai Academic Research Leader.
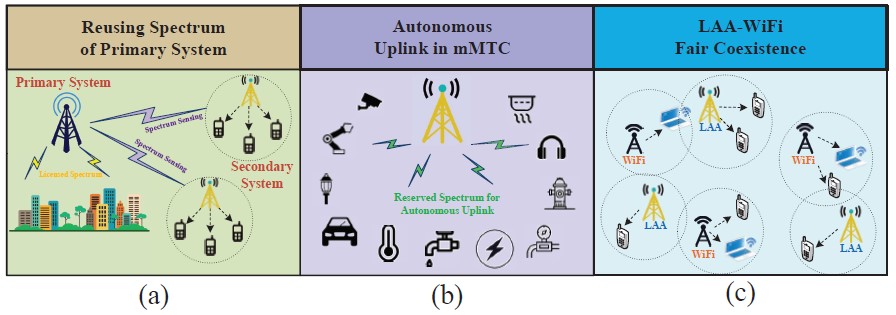
Three typical spectrum sensing involved scenarios in 5G communications: that is, throughput-oriented scenarios (a), energy saving-oriented scenarios (b), and sensing accuracy-oriented scenarios(c) (Image by SARI)
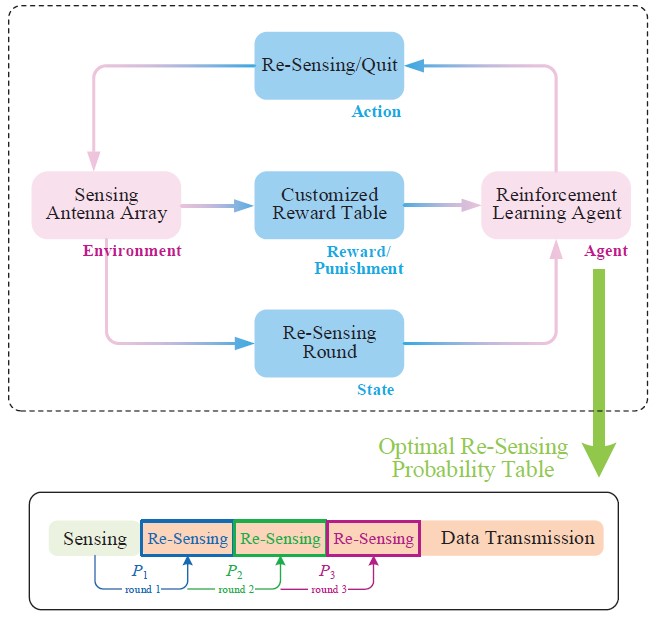
Reinforcement-learning-driven automatic repeat sensing mechanism (Image by SARI)
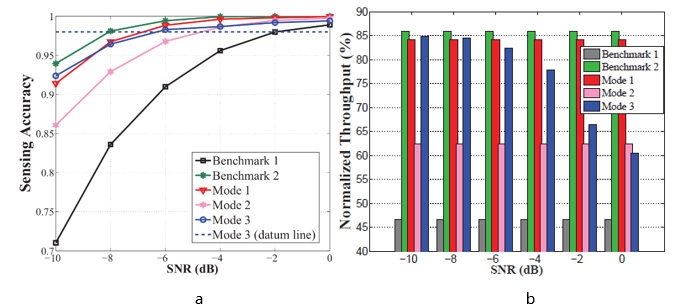
Performance comparison among three intelligent sensing strategies: a) Sensing accuracy performance; b) Throughput performance (Image by SARI)
Contact: HU Honglin
Shanghai Advanced Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email:huhl@sari.ac.cn





