Aromatics, in particular benzene, toluene, and xylenes, are important basic chemicals for highly valuable chemicals and materials.
Direct conversion of syngas to aromatics (STA) has drawn much attention and the current reported process can be achieved using tandem catalysts through the methanol or olefin intermediates. However, the development of efficient catalysts with high catalytic activity, selectivity, and stability still remains challenging.
Recently, a research group from Shanghai Advanced Research Institute(SARI) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has fabricated bifunctional catalysts combining versatile zeolites and CoMnAl oxide.
These catalysts exhibited high stability and high space-time yield of para-xylene under mild reaction conditions.
The study was published in Chem Catalysis on Feb. 14.
In order to produce a catalyst capable of converting syngas to aromatics selectively, the researchers first fabricated bifunctional catalysts containing a series of HZSM-5 zeolites and CoMnAl composite oxides (CMA).
The combined catalysts were tested in the STA reaction and the distribution of the aromatic products was tuned by modifying the HZSM-5 zeolite with a hollow nanostructure and a silicalite-1 layer grown epitaxially on the HZSM-5 crystals.
The results showed that the catalysts comprising CoMnAl catalysts and versatile HZSM-5@silicalite-1 zeolites achieved ultrahigh catalytic activity, selectivity, and stability under mild reaction conditions.
The CO conversion surpassed 70% under mild reaction conditions. The selectivity toward aromatics was higher than 63% and the para-xylene fraction of the aromatics produced reached 34.7%. In addition, the catalyst exhibited high stability, with no deactivation was observed over 726 h.
Furthermore, the researchers investigated the reaction mechanism and revealed that olefins and oxygen-containing aromatic compounds form were important intermediates inside HSZM-5 during the conversion of syngas to the aromatic products.
This study brings enlightenment for high-performance bifunctional catalyst for the direct conversion of syngas to value-added para-xylene. It also improves our understanding of the complex reaction network of syngas to aromatics, paving the way for designing highly active, selective, and stable catalysts for the synthesis of aromatics.
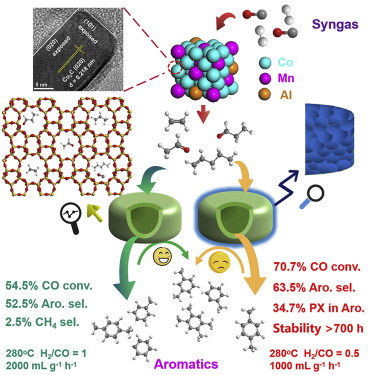
Schematic diagram of the syngas to aromatics pathway on CoMnAl/HZSM-5 bifunctional catalysts (Image by SARI)