Research Progress
While NOMA and spectrum sensing can ease the spectrum shortage, the combination of them does not reach the upper bound of spectrum utilization due to certain reasons. Also, it faces the challenge of detecting the signal states when multiple users superpose.
To address these problems, a collaborative research team led by Prof. XU Tianhong and HU Honglin from the Shanghai Advanced Research Institute (SARI) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in partnership with VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, the University of Electro-Communications in Japan, and Shanghai University, proposed an innovative NOMA-based spectrum sensing algorithm for uplink IoT networks, which improves the efficiency of targeting frequency usage in multi-user systems.
The research results were published in the latest issue of IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking.
Focusing on inter-system orthogonal/non-orthogonal aliasing coexistence scenarios, researchers propose an adaptive spectrum sensing technology for the multi-user uplink NOMA system, which harmonizes the advancements in both static and dynamic spectrum efficiency.
Moreover, researchers have derived the closed-form expressions among the number of primary users, user transmission willingness, the power ratio and the false-alarm probability in various sensing processes. These formulas have been validated through numerous simulations.
Furthermore, an adaptive NOMA-based sensing algorithm is designed and showcases an impressive 38.20% improvement in system throughput, compared with state-of-the-art techniques.
This research holds the promise of transforming the landscape of spectrum utilization in the emerging IoT era.
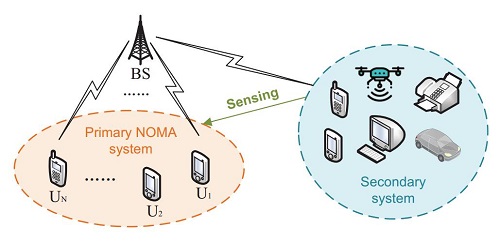
Schematic diagram of inter-system orthogonal/non-orthogonal aliasing coexistence IoT sensing scenarios (Image by SARI)
Contact: XU Tianheng
Shanghai Advanced Research Institute
Email: xuth@sari.ac.cn





