Research Progress
In a study published in The Innovation, Prof. WEI Wei, Prof. CHEN Wei and Prof. SONG Yanfang from Shanghai Advanced Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences constructed a hierarchical SnO2(101)@Ni composite hollow-fiber penetration electrode (HPE), which helped to realize high-efficiency CO2 electroreduction to formate in neutral electrolyte at ampere-level.
The electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction (eCO2RR), powered by renewable energy, is a promising method for converting CO2 into value-added products, thereby enabling sustainable carbon-neutral cycles. However, the practical implementation of eCO2RR technology is challenged by limitations in activity, selectivity, and stability.
To simultaneously achieve high formate Faradaic efficiency, high current density, and long-term stability, researchers constructed facet-oriented SnO2 nanoflowers arrayed on the exterior of three-dimensional nickel hollow fibers by a facile hydrothermal method.
This electrode demonstrates exceptional electrocatalytic performance for converting CO2 to formate.A formate selectivity of 94% and stability of 300 h with a current density of 1.3 A cm-2 at −1.1 V (vs. RHE) are attained under ambient conditions. Notably, an extremely high CO2single-pass conversion rate of 85% is achieved, outperforming prominent catalysts reported in electrocatalysis.
The synergetic combination of the unique nanostructures and their advanced spatial configuration is proposed to be responsible for the facet-oriented SnO2 with a hierarchical structure, providing fully exposed active sites and facilitating mass and charge transfers. Enhanced mass transfer in the hollow fiber electrode verified by electrochemical measurements and well-retained Sn4+species confirmed by in situ spectroscopy synergistically boost the high CO2conversion activity. In situ spectroscopy and theoretical calculation results demonstrate that theSnO2(101) facet favors *OCHO intermediate formation and *HCOOH desorption, leading to high formate selectivity.
This study provides a straightforward approach to the precise fabrication of composite hollow fiber electrodes, enabling highly efficient electrocatalytic reactions with gas molecules.
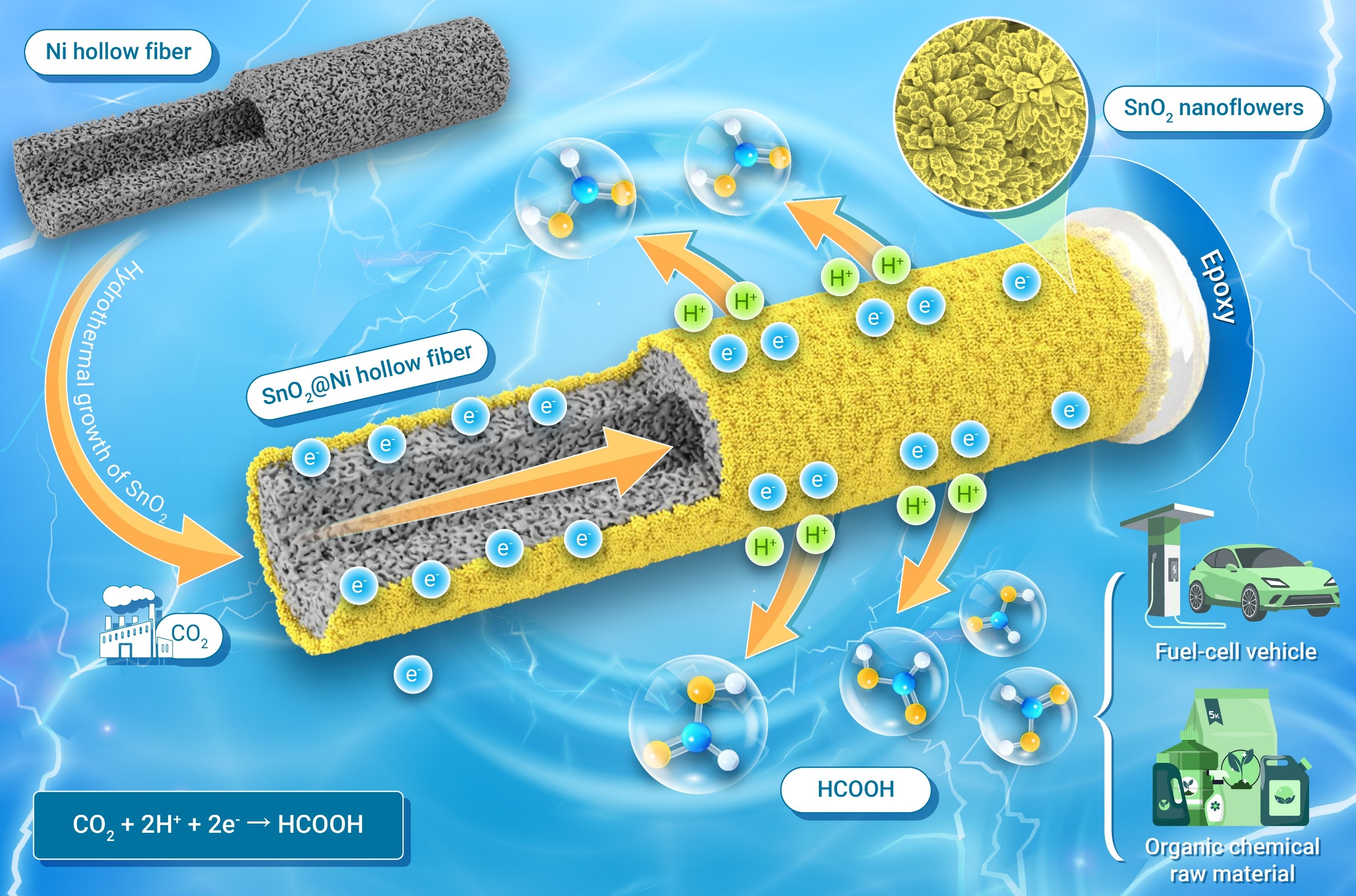
Schematic diagram of electroreduction of CO2 to formate over SnO2@Ni hollow fiber penetration electrode (Image by SARI)





