Research Progress
New Framework Proposed for Analyzing the Fouling/Scaling behavior of MD Membrane
A research team led by Prof. HE Tao proposed a hydrodynamic theory of slippery surface for fouling/scaling resistance of superhydrophobic membranes.The latest result on the hydrodynamic behavior and scaling/fouling resistance of MD membranes was published in Desalination.
Researchers Reveal In-situ Manipulation of Active Au-TiO2 Interface
An international joint research team reported an in-situ strategy to manipulate interfacial structure with atomic precision during catalytic reactions. Results were published in the latest issue of Science.
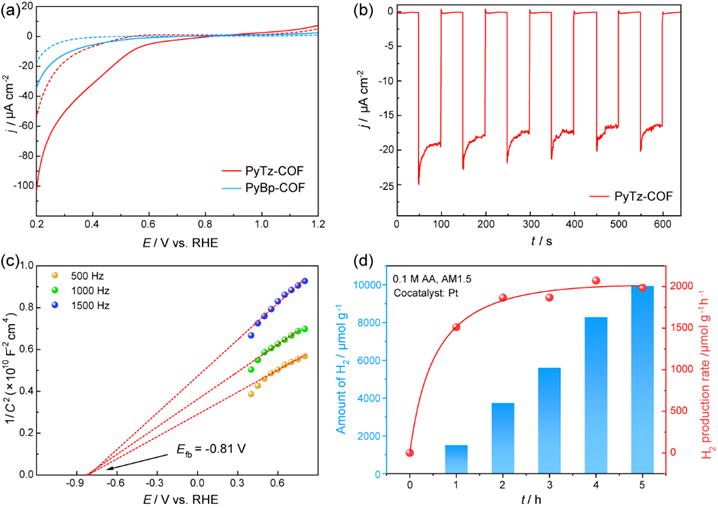
Researchers Develop a Novel Donor-Acceptor System for Highly-effective Sunlight-Driven Hydrogen Evolution
a research team reported a novel photoactive 2D COF from donor Py and acceptor Tz building units, which enabled remarkable photogenerated charge separation and efficient charge migration.
Scientists Reveal New Tools in Single-cell Infrared Microspectroscopy Based on Synchrotron Radiation
Single-cell technologies are becoming hot topics and key directions of biomedical research due to their abilities to answer the basic question of cellular functional heterogeneity and to interpret the molecular basis of various chronic diseases as well as aging. Among the single cell techniques, single-cell infrared spectroscopy obtains growing attention because of its advantages in simultaneously identifying the characteristics of intracellular metabolites. Recently, research team at Shanghai Advanced Research Institute together with collaborators have successfully revealed new tools to evaluate single-cell infrared data based on synchrotron radiation.
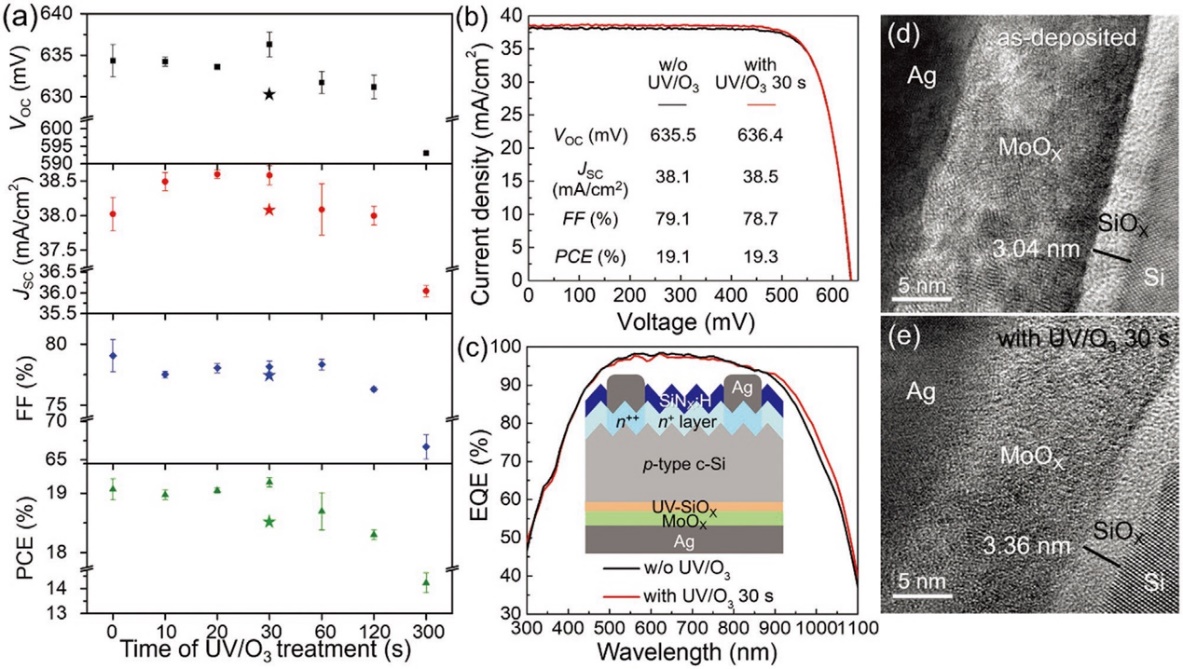
Novel compound/c-Si passivation contact for p‐Type Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells Achieving 20% Efficiency
Crystalline silicon heterojunction solar cells based on hole-selective MoOX contacts provide obvious merits in terms of the decent passivation and carrier selectivity but face the challenge of long-term stability. With the aim to improve the performance and stability of solar cells with full area MoOX/ metal contacts, a SiOX tunneling layer on silicon surface is intentionally formed by UV/O3 treatment and an indium tin oxide (ITO) film is sputtered as a high-work-function electrode.

Researchers Develop Integrative Treatment of Tumor-related Bone Defects
Malignant bone tumors have caused great obstacles and serious illnesses for tumor recurrence and difficulty in reconstructing and repairing large defeats after tumorectomy due to the poor prognosis for metastatic relapse or recurrence for patients with the axial disease. In a study published in Chemical Engineering Journal, a research team from the Shanghai Advanced Research Institute (SARI) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) reported a novel therapeutic treatment of anti-tumor/bone repair by combination of MoS2 nanosheets with 3D printed bioactive borosilicate glass scaffolds.





