Research Progress
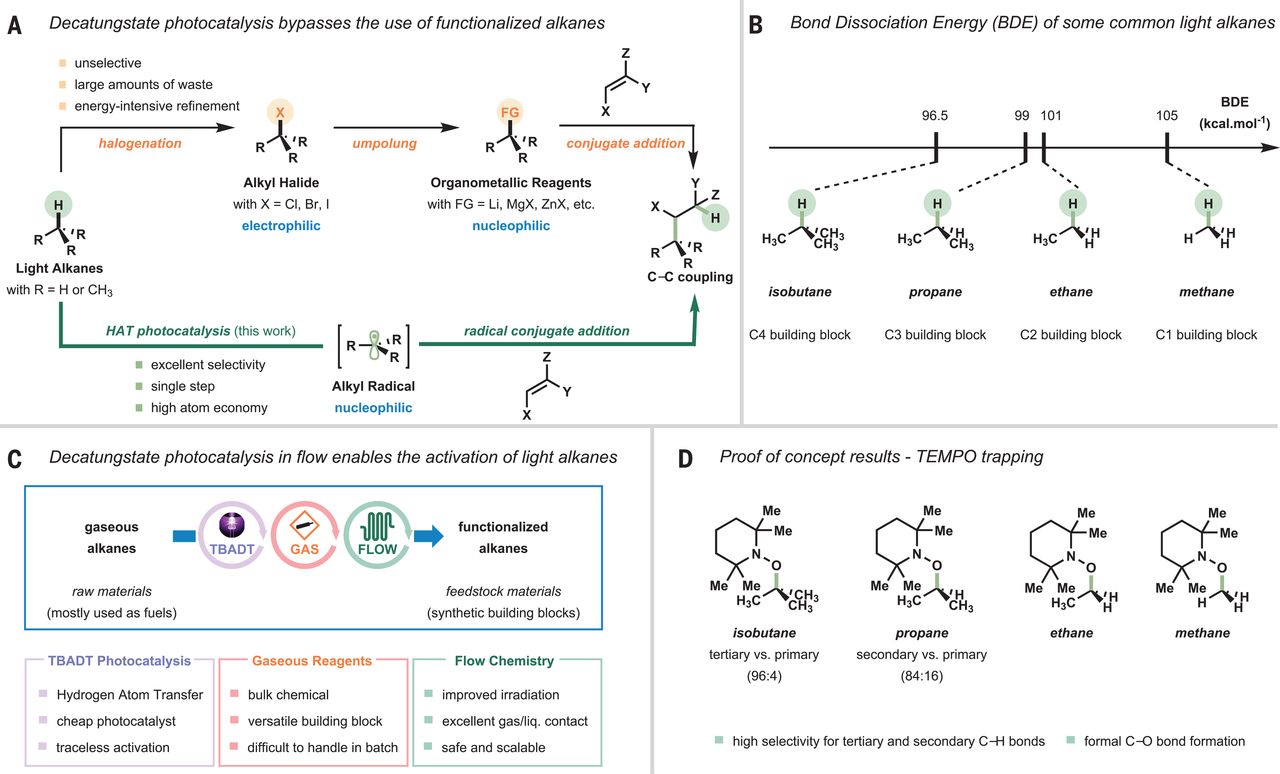
New Light-based Method Proposed for C(sp3)–H Functionalizations of Light Hydrocarbons
Intrinsic inertness of gaseous hydrocarbons requires harsh reaction conditions to enable C(sp3)–H bond cleavage, resulting in low-yielding and unselective transformation to high-value added chemicals. Motivated by such a challenge, a team collaborated by researchers from Eindhoven University of Technology, ShanghaiTech University and Shanghai Advanced Research Institute (SARI) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported a general and mild strategy to directly activate alkanes using decatungstate photocatalysis in flow.
NOW OPEN: The expression plasmids for all 29 proteins encoded by the COVID-19 virus are available for request
Now, expression plasmids for all these 29 proteins are available to global scientists through a Protein Bank Program (PBP) launched by the National Facility for Protein Science in Shanghai (NFPS).

Efficient Indium Oxide Catalysts Designed for CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol
Catalytic hydrogenation of carbon dioxide is a green and sustainable means of synthesizing commodity chemicals such as methanol.Recent studies revealed the potential for a family of metal oxides to catalyze this reaction. However, further optimizing their catalytic performance for industrial applications remained a great challenge.A team at the Shanghai Advanced Research Institute (SARI) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported a successful case of theory-guided rational design of indium oxide (In2O3) catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol with high activity and selectivity.
SSRF Helps on the COVID-19 Structure Determination to Understand the Infection Mechanism and Drugs R&D
To meet the urgent needs of determining the protein structure, Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF) has opened a green channel to fully support the research teams carrying out studies related to COVID-19. At the end of January, SSRF promptly rebooted the accelerator that was shut down for maintenance. Three protein crystallography beamlines reopened: BL17U1, BL18U1 and BL19U1, which also played a significant role in the studies of the previous epidemic like H1N1, H7N9, MERS, Zika, and Ebola.
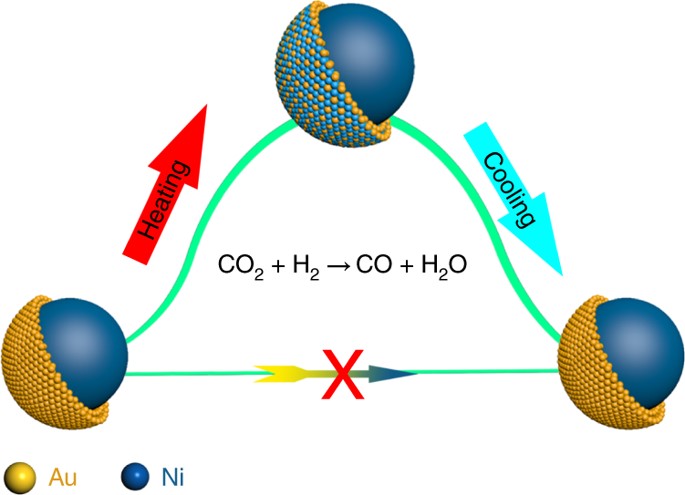
Researchers Reveal a Dynamic Mechanism for Ni–Au Bimetallic Nanoparticles during CO2 Hydrogenation
The high catalytic performance of core–shell nanoparticles (NP) is usually attributed to the syngergy of distinct geometric and electronic structures. Although the general assumption is that core–shell NPs maintain their configuration under working conditions, it remains unclear whether they maintain their structure throughout a reaction.Scientists recently reported a different working mechanism and demonstrated that the core–shell structure may not exist under a specific set of conditions, which overturns the conventional understanding.
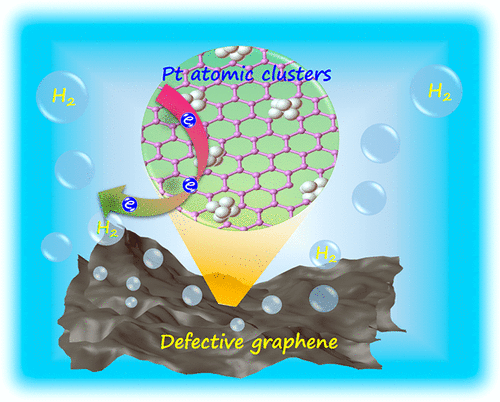
Novel Approach to Pt Electroless Deposition for Highly Efficient Hydrogen Evolution
The small size and large specific surface area intrinsically associated with Pt atomic clusters pose challenges in the synthesis and stabilization of Pt-ACs without agglomeration. A research team reported a novel one-step carbon-defect-driven electroless deposition (ELD) method to produce ultrasmall but well-defined and stable Pt-ACs supported by defective graphene (Pt-AC/DG) structures.





