Research Progress
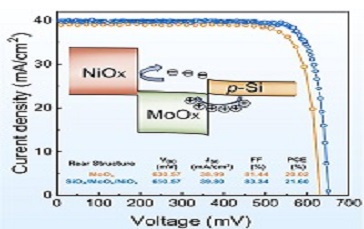
Scientists Propose Novel Bilayer Structure for Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells
Researchers from the Shanghai Advanced Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have proposed a novel “bilayer” structure composing of different transition metal oxide (TMO) thin films in crystalline silicon (c-Si) solar cells in order to improve the cells’ efficiency.
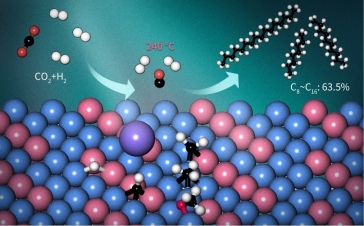
Scientists Achieved Direct Conversion of CO2 to a Jet Fuel over CoFe Alloy Catalysts
Direct conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) using green hydrogen is a sustainable approach to jet fuel production. However, achieving a high level of performance remains a challenge due to the inertness of CO2 and its low activity for subsequent C–C bond formation. a research team led by Prof. Gao Peng, Prof. Li Shenggang and Prof. Sun Yuhan at Shanghai Advanced Research Institute (SARI) reported a Na-modified CoFe alloy catalyst using layered double-hydroxide precursors that directly transforms CO2 to a jet fuel composed of C8-C16 jet-fuel-range hydrocarbons with very high selectivity.
Scientists Reveal the Uniqueness of Ullmann Reaction Path
a research team reported that the Ullmann reaction path is unique regardless of predesigned assembled structures, dominated by the fact that weak intermolecular interaction in assembled nanostructures is suppressed by strong covalent bonding during reactions.
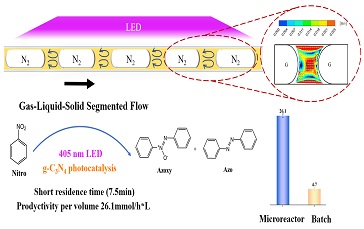
Researchers Develop a Novel Approach to Heterogeneous Photosynthesis of Azo- Compounds in Continuous Flow
a research team reported a novel approach of gas-liquid-solid segmented flow, which enabled utilizing the solid photocatalysis in continuous flow without clogging. Owning to the inner recirculation in liquid segments and the formed thin film, this method ensures the effective suspension of solid catalysts in flow, resulting in enhanced mass transfer and irradiation.
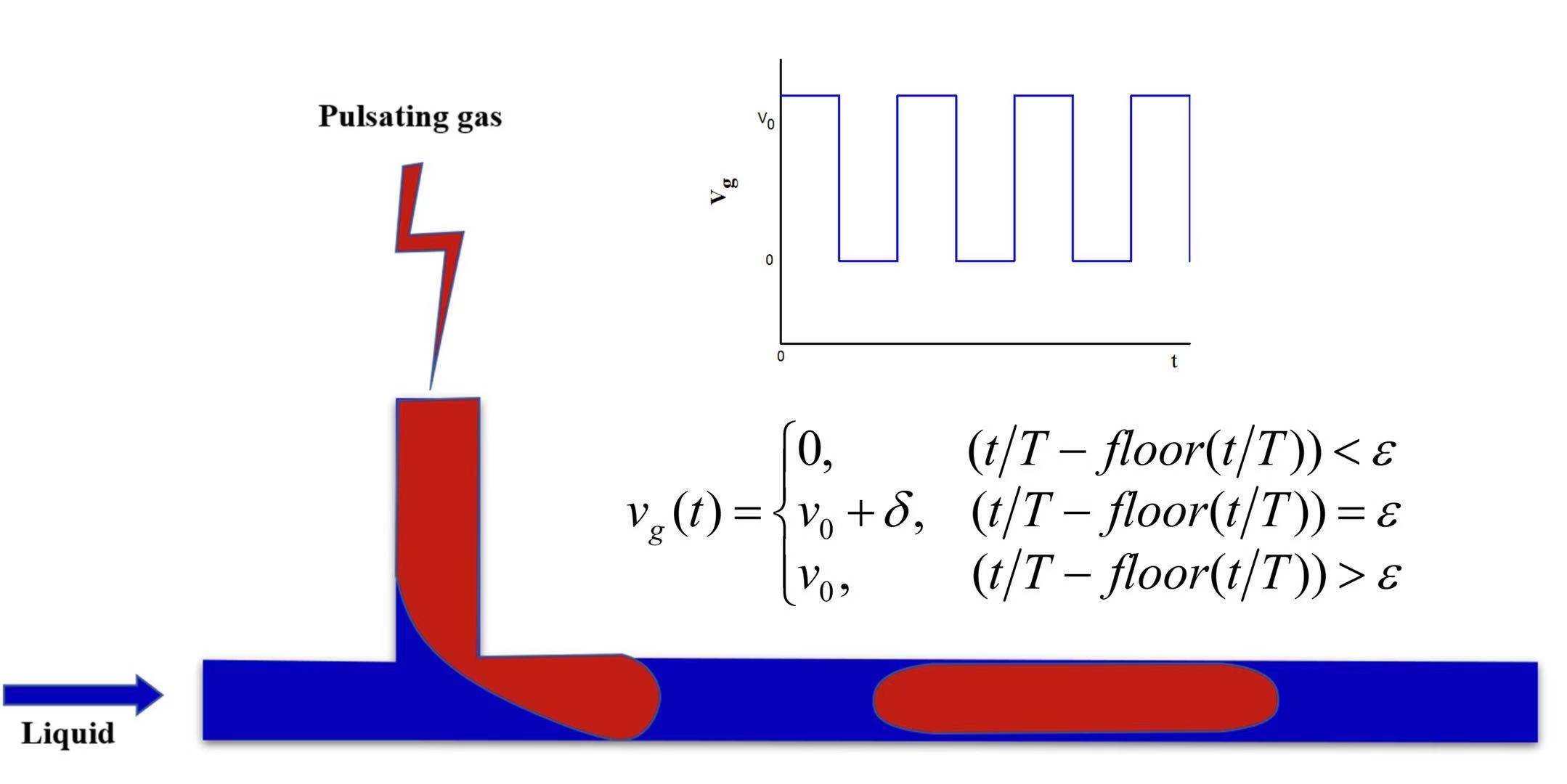
Researchers Propose a Novel Approach to Precisely Control the Gas-liquid Taylor Flow Pattern for Continuous Flow Chemistry
A research team reported a novel approach of adding pulsation field to precisely regulate the gas-liquid Taylor Flow.
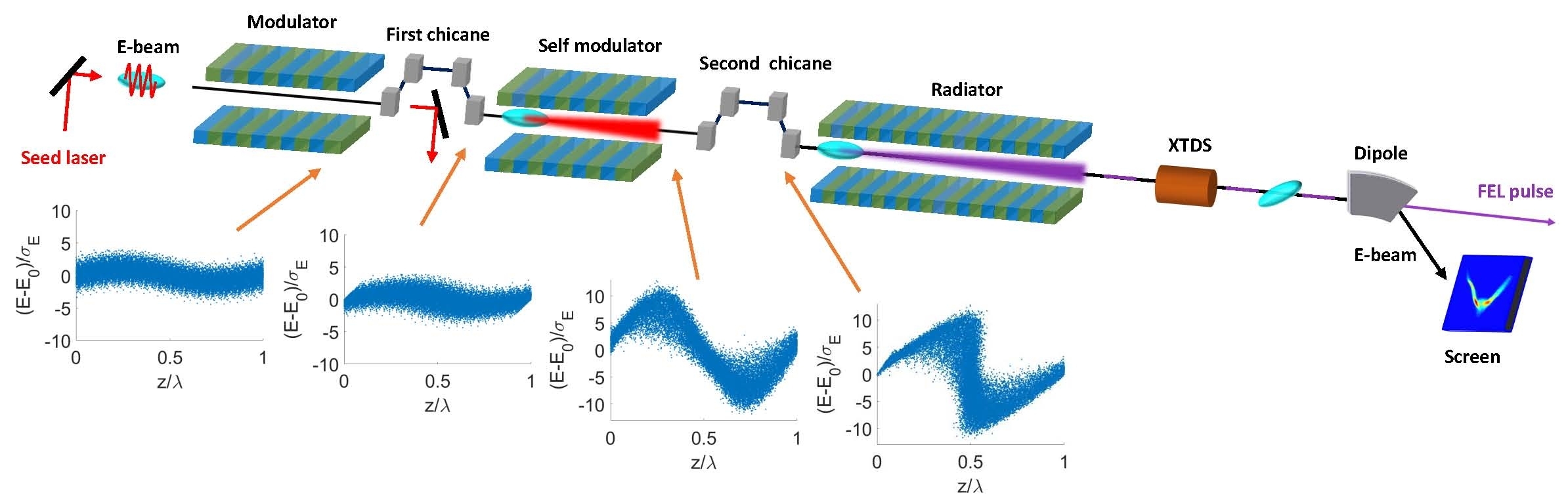
Scientists Propose a Novel Self-modulation Scheme in Seeded Free-Electron Lasers
The FEL teams at Shanghai Advanced Research Institute and Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences collaborated and reported a novel self-modulation method for enhancing laser-induced energy modulation, thereby significantly reducing the requirement of an external laser system.





